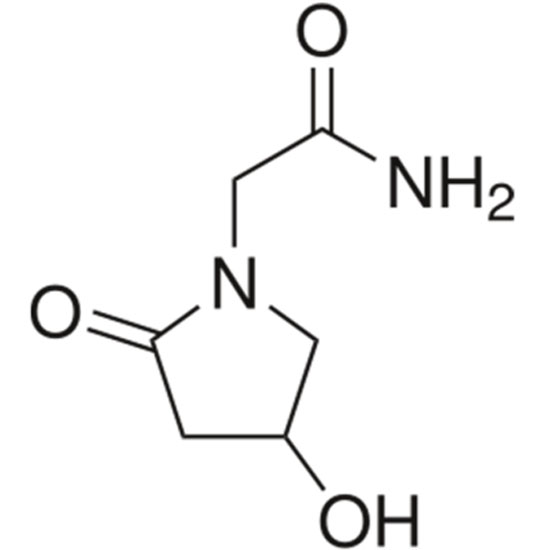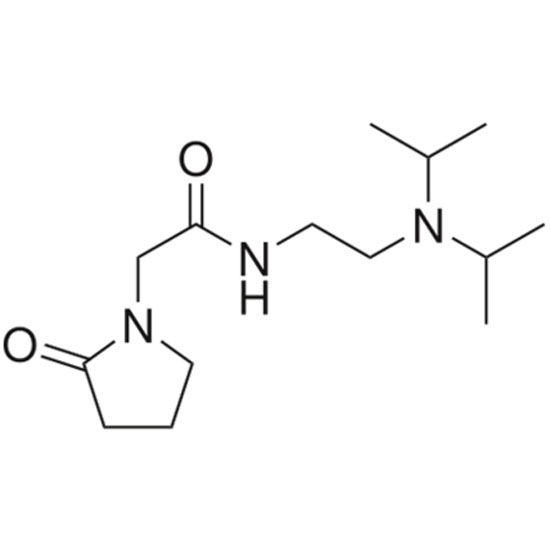

Coluracetam
Coluracetam (code name BCI-540; formerly MKC-231) is a nootropic agent of the racetam family. It was initially developed and tested by the Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation for Alzheimer's disease.
Coluracetam enhances high-affinity choline uptake, which is the rate-limiting step of acetylcholine synthesis. Studies have shown coluracetam to improve learning impairment on a single oral dose given to rarts which have been exposed to cholinergic neurotoxins. Subsequent studies have shown that it may induce long-lasting procognitive effects in cholinergic neurotoxin-treated rats by changing the choline transporter regulation system.
Coluracetam enhances high-affinity choline uptake, which is the rate-limiting step of acetylcholine synthesis. Studies have shown coluracetam to improve learning impairment on a single oral dose given to rarts which have been exposed to cholinergic neurotoxins. Subsequent studies have shown that it may induce long-lasting procognitive effects in cholinergic neurotoxin-treated rats by changing the choline transporter regulation system.