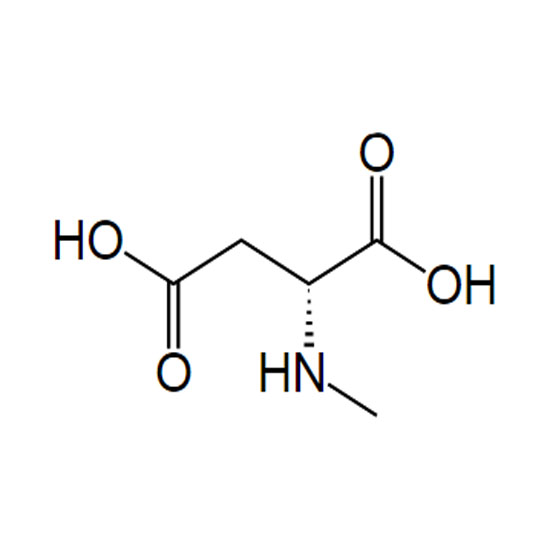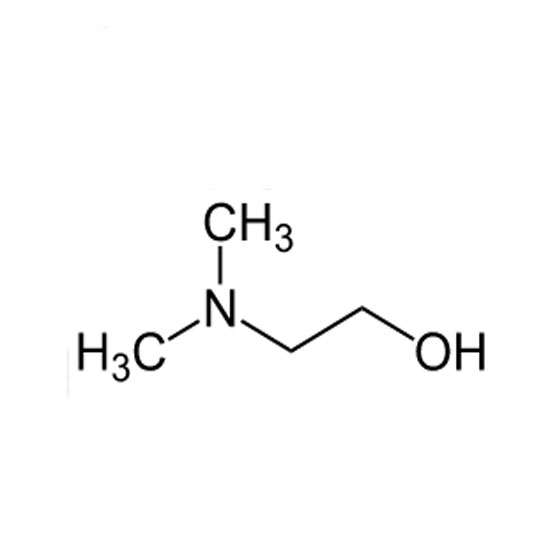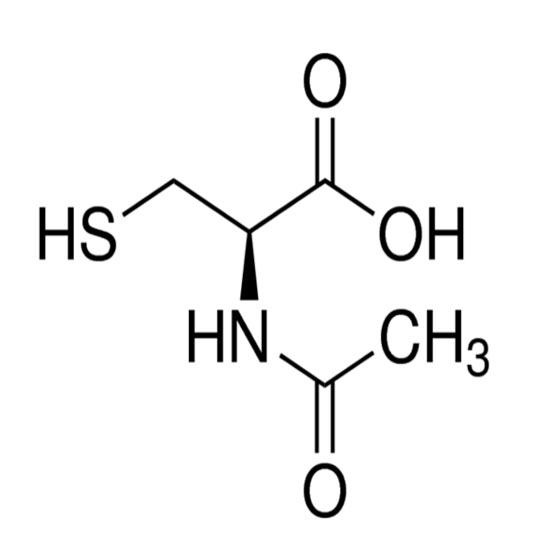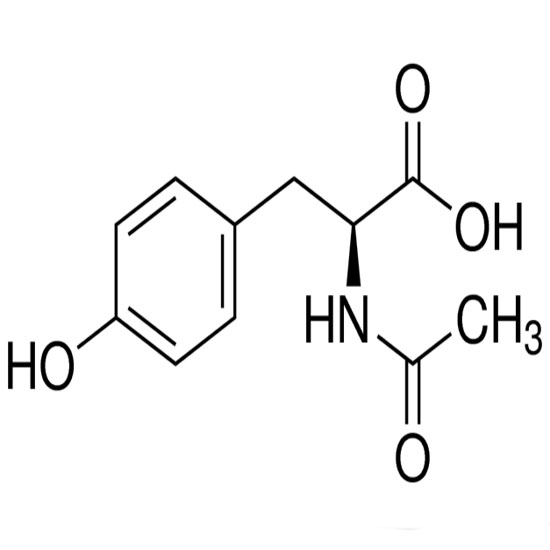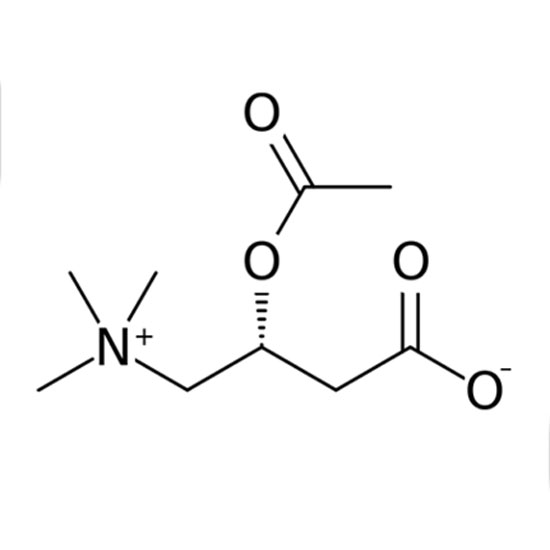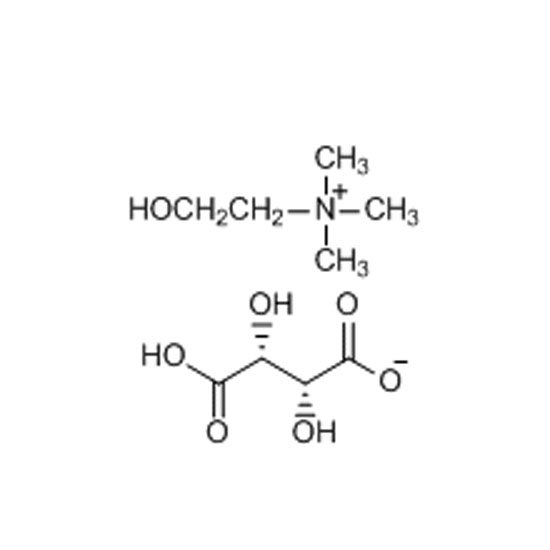

The cation appears in the head groups of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin, two classes of phosolipid that are abundant in cell membranes. Choline is the precursor molecule for the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is involved in many functions including memory and muscle control.
Some animals cannot produce choline, but must consume it through their diet to remain healthy. Humans make choline in the liver. Whether dietary or supplementalcholine is beneficial or harmful to humans is undefined. Possible benefits include reducing the risk of neural tube defects and fatty liver disease. It has also been found that intake of choline during pregnancy can have long-term beneficial effects on memory for the child.